AQW-051
CAS No. 669770-29-0
AQW-051 ( AQW051 | AQW 051 )
产品货号. M15558 CAS No. 669770-29-0
AQW-051 是一种新型、有效、选择性、口服生物利用度、脑渗透性 α7 nAChR 部分激动剂,pKd 为 7.56。
纯度: >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| 规格 | 价格/人民币 | 库存 | 数量 |
| 5MG | ¥648 | 有现货 |

|
| 10MG | ¥1126 | 有现货 |


|
| 25MG | ¥2341 | 有现货 |


|
| 50MG | ¥3686 | 有现货 |


|
| 100MG | ¥5443 | 有现货 |


|
| 500MG | ¥11583 | 有现货 |


|
| 1G | 获取报价 | 有现货 |


|
生物学信息
-
产品名称AQW-051
-
注意事项本公司产品仅用于科研实验,不得用于人体或动物的临床与诊断
-
产品简述AQW-051 是一种新型、有效、选择性、口服生物利用度、脑渗透性 α7 nAChR 部分激动剂,pKd 为 7.56。
-
产品描述AQW-051 is a novel, potent and selective, orally bioavailable, brain-penetrant α7 nAChR partial agonist with pKd of 7.56; displays high selectivity (>100-fold) over other nACh receptors; stimulates calcium influx in GH3–ha7-22 cells recombinantly expressing the human α7-nACh receptor with pEC50 of 7.41; facilitates learning/memory performance in mice; reduces l-Dopa-induced dyskinesias and extends the duration of l-Dopa effects in parkinsonian monkeys.Parkinson Disease Phase 2 Clinical.
-
体外实验——
-
体内实验Animal Model:OF1/IC strain adult miceDosage:0.03 and 0.3 mg/kg Administration:Oral administration; 0.03 and 0.3 mg/kg once Result:Increased the learning/memory performance with more time to scrutinize the novel partner than the familiar partner during the re-test trial at 24 h. Showed cognitive-enhancing effects in mice by the object recognition test (ORT).
-
同义词AQW051 | AQW 051
-
通路Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
靶点nAChR
-
受体nAChR
-
研究领域Neurological Disease
-
适应症Parkinson Disease
化学信息
-
CAS Number669770-29-0
-
分子量294.398
-
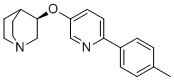
分子式C19H22N2O
-
纯度>98% (HPLC)
-
溶解度In Vitro:?DMSO : 16.67 mg/mL (56.63 mM)
-
SMILESCC1=CC=C(C2=CC=C(O[C@H]3CN4CCC3CC4)C=N2)C=C1
-
化学全称(3R)-3-{[6-(4-methylphenyl)pyridin-3-yl]oxy}-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane
运输与储存
-
储存条件(-20℃)
-
运输条件With Ice Pack
-
稳定性≥ 2 years
参考文献
1. Feuerbach D, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;172(5):1292-304.
2. Di Paolo T, et al. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014 Nov;20(11):1119-23.
3. Beinat C, et al. CNS Drugs. 2015 Jul;29(7):529-42.
4. Trenkwalder C, et al. Mov Disord. 2016 Jul;31(7):1049-54.



 021-51111890
021-51111890 购物车(0)
购物车(0)
 sales@molnova.cn
sales@molnova.cn